New SBD & MOSFET Packages Slash Size, Increase Power Density
Article
Size matters in almost any application, as does efficiency. For instance, in enterprise data centers, a significant portion of the upfront costs are due to building floor space, and most operational costs are from utility electricity. Or consider the very different industrial power and motor-drive applications in which careful trade-offs among size, weight, efficiency, and cost are needed for success.
Indeed, the pressure to improve power density is only increasing. Traditional data centers that use about 10 kW per rack are no longer sufficient for demanding end-use applications like high-performance computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.i

A similar trend is true for industrial applications, wherein increasing demand for smaller size and weight and lower cooling requirements requires higher efficiency and higher power density.
Wide-bandgap semiconductor technologies, like Wolfspeed’s Silicon Carbide (SiC) MOSFETs and Schottky Barrier Diodes (SBDs), allow power designers to utilize several advantages compared with silicon. Lower conduction and switching losses increase efficiency, and high-frequency operation helps reduce the size of passive components — inductors, capacitors, and transformers. Their high-junction–temperature capabilities allow the use of smaller thermal management solutions. By supporting high-voltage operation, such as 650 V or more, Wolfspeed’s products also help reduce the number of switches required in high-voltage applications.
The net result is improved system-level efficiency and power density at lower system-level cost.
Package matters
These advantages, however, put pressure on packaging technology so that it capably supports device performance rather than hinders it. Common packaging challenges include:
• Keeping parasitics in check
• Reducing package size without sacrificing thermal performance
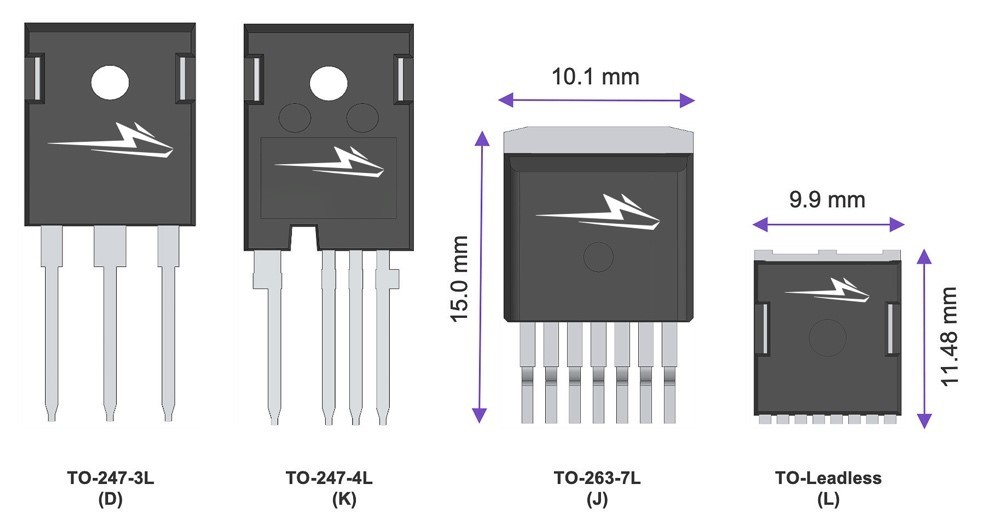
To address market demand for high power density, Wolfspeed has introduced new, smaller surface-mount packages for its discrete SiC Schottky diodes and MOSFETs. The company’s C6D 650 V SiC Schottky diodes are now available in QFN 8 × 8 and their C3M SiC discrete MOSFETs are now sampling in a TO lead-less (TOLL) package that is considerably smaller than the other options of TO-247-3, TO-247-4, and TO-263-7.
Traditional through-hole packages, such as the TO-247, can pose assembly automation challenges for some high-volume system producers. If all devices on the board are surface-mount (SMDs), assembly can be accomplished in a single automated step. This has a significant impact toward reducing production costs.
Schottky diodes in 8 × 8 QFN
The new diodes with the package ID “Q” — C6D06065Q, C6D08065Q, and C6D10065Q — have a 60% smaller footprint compared with the standard TO-263-2L with package ID “G” in the SKU (Figure 1). Compared with this TO-263-2L or D2PAK, the new QFN 8x8 devices have an 80% reduction in height. Overall, these footprint reductions make the QFN highly advantageous to low-profile applications.
The SiC SBD technology also enables a low forward-voltage drop (VF) of 1.27 V at 25˚C and 1.37 V at 175˚C, thereby reducing forward power losses. This allows designers to achieve the highest possible system-level efficiencies in applications like PFC boost converters.
The QFN package offers a lower lead inductance, which is critical to reducing switching losses in the final system and enabling high-frequency operation. By allowing higher switching frequencies, the parts enable higher power densities to be achieved. The QFN packages also incorporate efficient thermal management with bottom-side cooling (Figure 2).
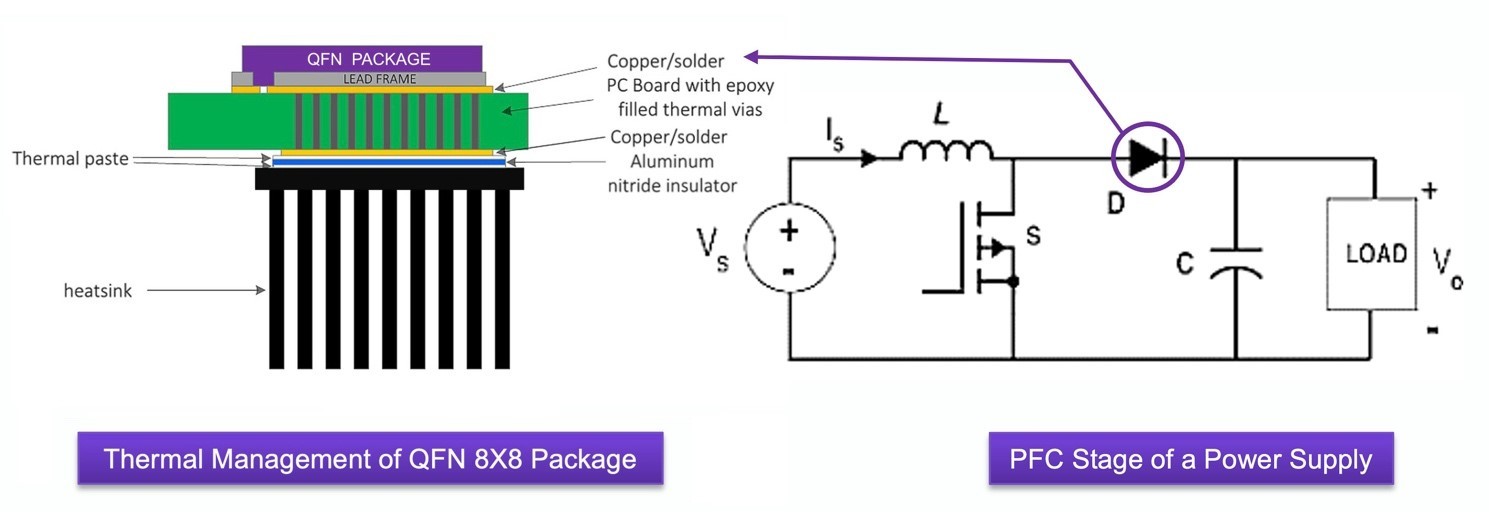
All devices feature a creepage distance that is suitable for applications with an operating voltage of 400 V. The parts offer continuous forward current (IF) ratings of 6 A, 8 A, and 10 A and junction-to-case thermal resistance (Rθ, JC) as low as 1.4˚C/W.
TOLL-packaged Silicon Carbide MOSFETs
The surface-mount TOLL is an innovative package that the industry is adopting typically for high-current, high-power–density applications. Wolfspeed’s industrial-application–qualified 650 V SiC MOSFETs in the TOLL package are significantly smaller than other package options (Figure 3). Compared with the standard TO-263-7L’s footprint of 151.5 mm2 and height of 4.30 mm, the TOLL device has a footprint of 113 mm2 and height of 2.2 mm. That is a nearly 25% reduction in footprint and an even more remarkable 50% reduction in height.
Wolfspeed’s TOLL package also features a low source inductance that allows designers to utilize lower external gate resistance, which not only reduces the switching losses but helps avoid peak voltage overshoots during turn-off. The parts are therefore well-suited to high switching frequency applications, which can help increase power density by reducing the size of magnetic components.
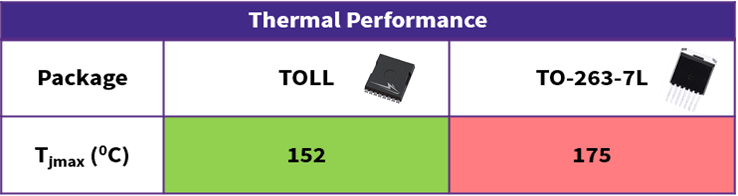
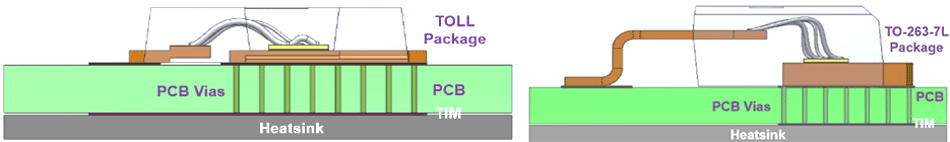
To address thermal management requirements from a package of this size, the new TOLL devices have much larger back metal tabs to help lower device junction temperature (Tjmax). In thermal simulations, shown in Figure 4, the package was tested for dissipating 28 W with convection cooling at 5,000 W/m2K. The TOLL device could keep Tjmax as low as 152˚C compared with TO-263-7L’s 175˚C. Designs using these devices would therefore require less thermal management, granting cost, space, and weight benefits to the application.
The TOLL devices also have a minimum creepage of 3.5 mm (D-S) that is ideal for ~400VDC operation. The MOSFETs — PC3M0045065L, PC3M0060065L, and PC3M0120065L — are offered in three RDS(ON) options of 45 mΩ, 60 mΩ, and 120 mΩ, with rated drain currents (ID) of 50 A, 36 A, and 21 A, respectively.
This makes the switches suitable for a wide range of applications, including server/telecom power supplies, consumer/computing/industrial SMPS, solar power inverters, motor drives, light EVs, battery chargers, and home appliances.
Path to cooler, smaller devices
Wolfspeed’s new SMD power devices not only save precious application space but dissipate heat more efficiently, which helps deliver on lower production costs, lower thermal solution costs, and higher power densities.
Visit Wolfspeed’s 650 V Silicon Carbide Schottky Diode and Silicon Carbide MOSFETs product pages to find parts that best suit your design goals.
Featured Products
Discrete SiC MOSFETs
Discrete SiC MOSFETs
Discrete SiC MOSFETs
Product SKU | Buy Online | Request Sample | Data Sheet | CAD Model | Blocking Voltage | RDS(ON) at 25°C | Generation | Current Rating | Gate Charge Total | Output Capacitance | Total Power Dissipation (PTOT) | Tjmax | Package | Qualification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
650 V | 120 mΩ | Gen 3 | 21 A | 26 nC | 45 pF | 86 W | 175 °C | TOLL | Industrial | |||||
650 V | 60 mΩ | Gen 3 | 39 A | 46 nC | 72 pF | 131 W | 175 °C | TOLL | Industrial | |||||
650 V | 45 mΩ | Gen 3 | 49 A | 59 nC | 101 pF | 164 W | 175 °C | TOLL | Industrial |
End of Section
Discrete SiC Schottky Diodes
Discrete SiC Schottky Diodes
Discrete SiC Schottky Diodes
Product SKU | Buy Online | Request Sample | Data Sheet | Blocking Voltage | Current Rating | Generation | Forward Voltage(VF(type)) | Maximum Continuous Current (IF) | Total Capacitive Charge (QC (typ)) | Total Power Dissipation (PTOT) | Package | Qualification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
650 V | 6 A | Gen 6 | 1.27 V | 6 A | 23 nC | 69 W | QFN 8x8 | Industrial | ||||
650 V | 8 A | Gen 6 | 1.27 V | 8 A | 29 nC | 92 W | QFN 8x8 | Industrial | ||||
650 V | 10 A | Gen 6 | 1.27 V | 10 A | 34 nC | 119 W | QFN 8x8 | Industrial |
End of Section
i Data Centre Dynamics Ltd, Increasing density: the new data center reality. Source: https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/opinions/increasing-density-the-new-data-center-reality/